Semiconductor Laboratory Course Diodes
The I-V Characteristic Curves, which is short for Current-Voltage Characteristic Curves or simply I-V curves of an electrical device or component, are a set of graphical curves which are used to define its operation within an electrical circuit.
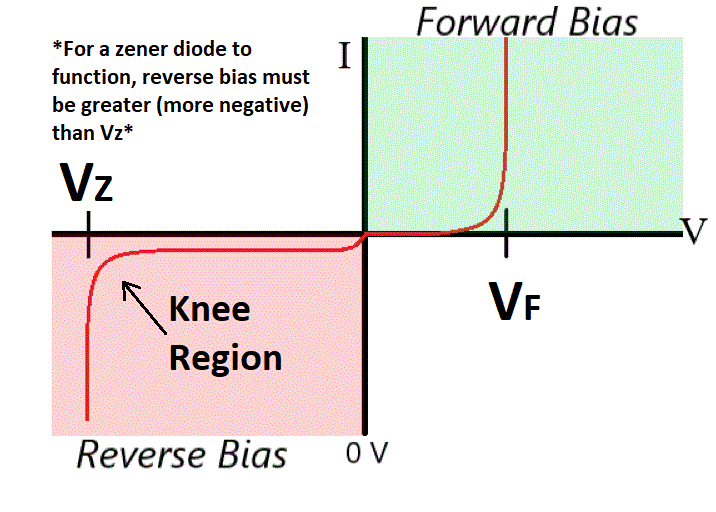
Zener Diode Voltage Regulator Electronics Reference
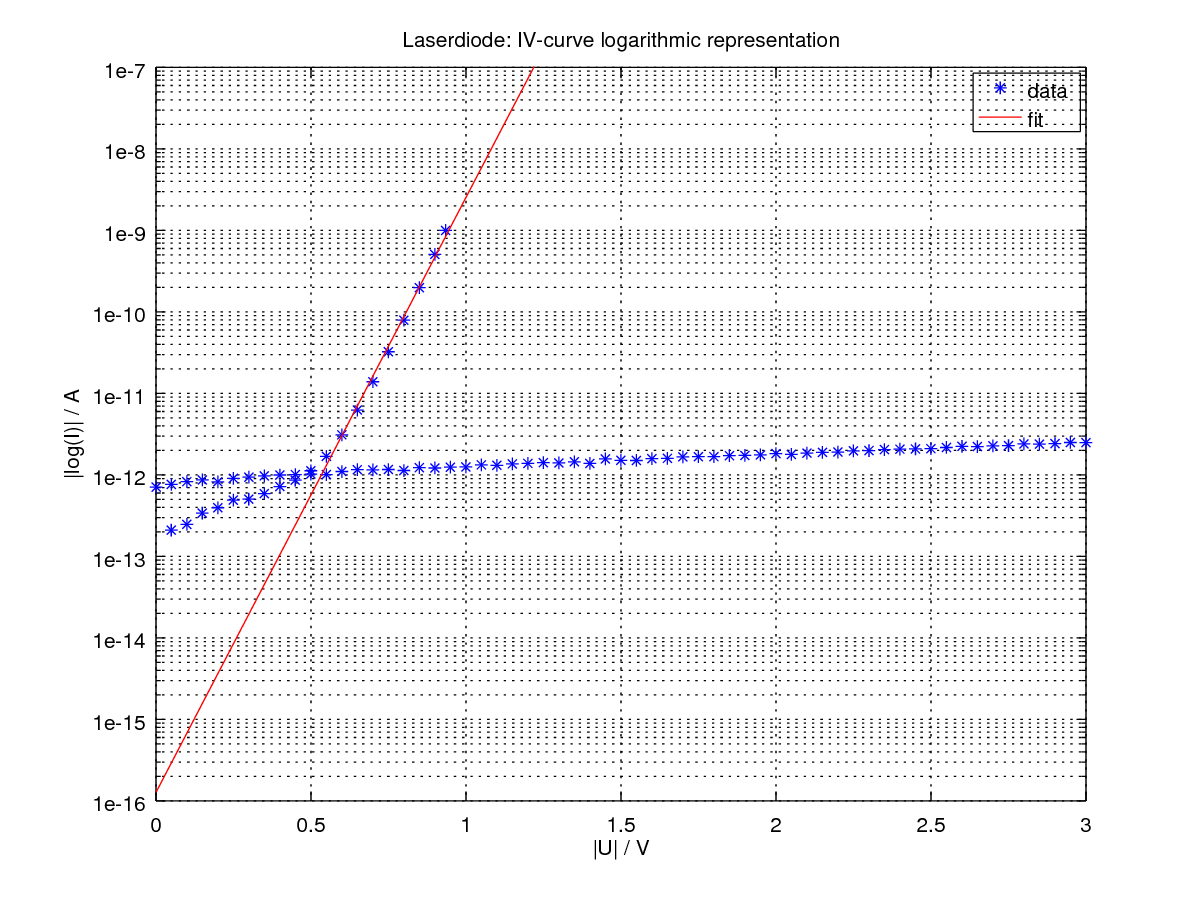
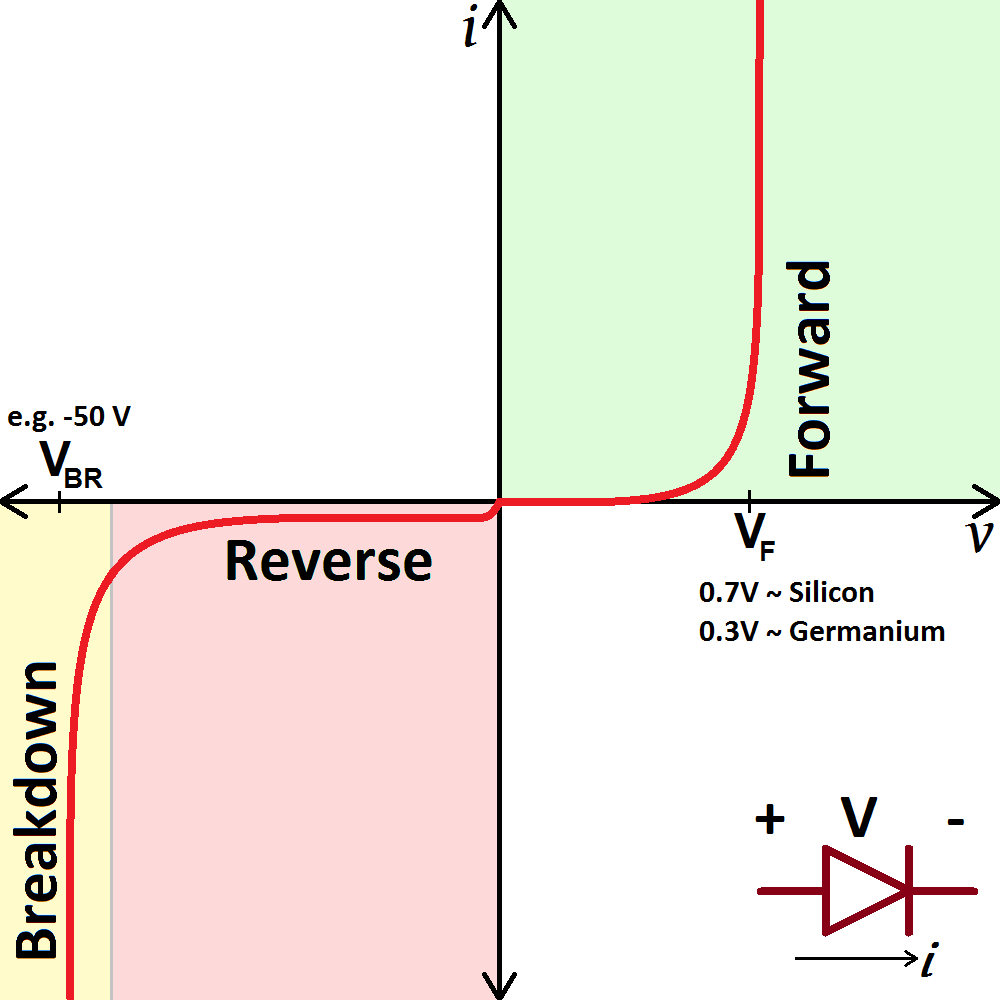
Such an I-V curve can be extended on the left side of the graph, meaning with negative voltages applied on the device under test. Here, with the example of a diode, a reversed voltage means that the diode is reverse biased, and no current will circulate. The plot will stay close to the horizontal axis as I=0.
Diode Iv Curve With Temperature
As we can see, the general shape of the metal-semiconductor Schottky diode I-V characteristics is very similar to that of a standard pn-junction diode, except the corner or knee voltage at which the ms-junction diode starts to conduct is much lower at around 0.4 volts.

IV Curve Measurement How to Measure Solar Cell IV Curve Ossila
Current Circuit: Diode I/V Curve This example shows the I/V curve of a diode. With a resistor, I (current) and V (voltage) are proportional (by Ohm's Law). With a diode, I and V have an exponential relationship. At the lower left, voltage is shown in green, and current in yellow.
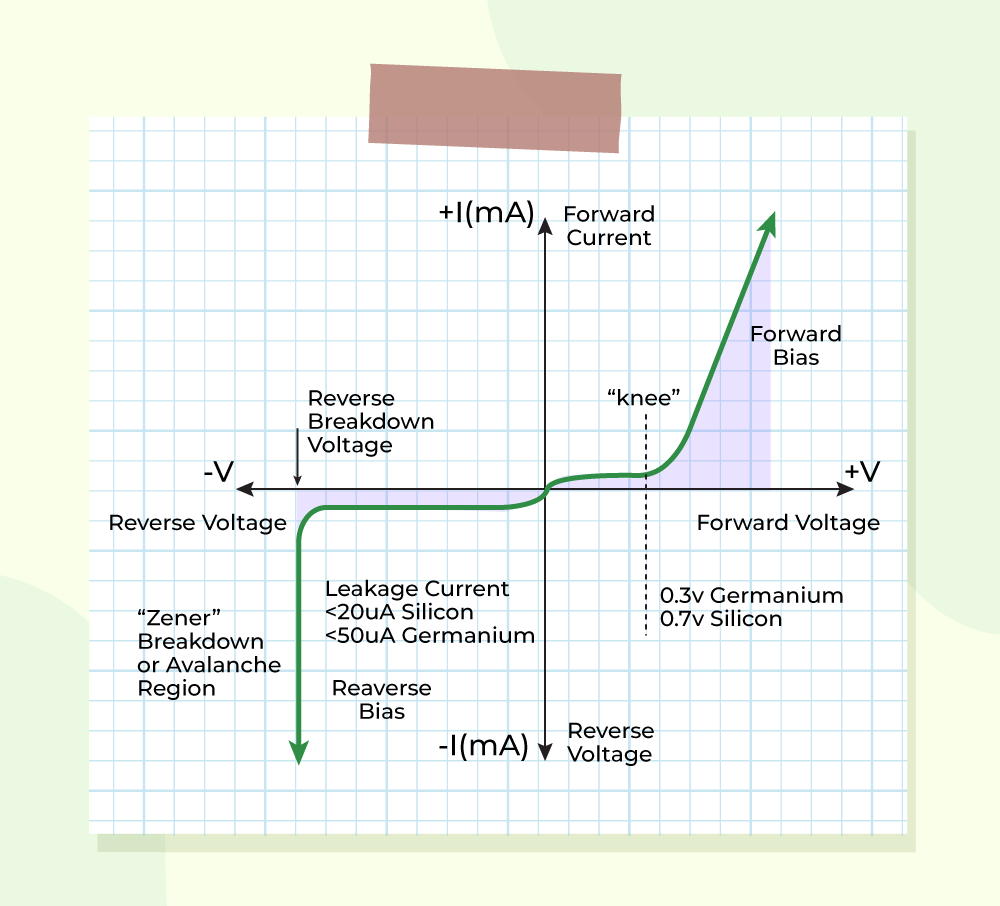
pn Junction Diode Definition, Formation, Characteristics, Applications
The IV curve of a solar cell is the superposition of the IV curve of the solar cell diode in the dark with the light-generated current. 1 The light has the effect of shifting the IV curve down into the fourth quadrant where power can be extracted from the diode.
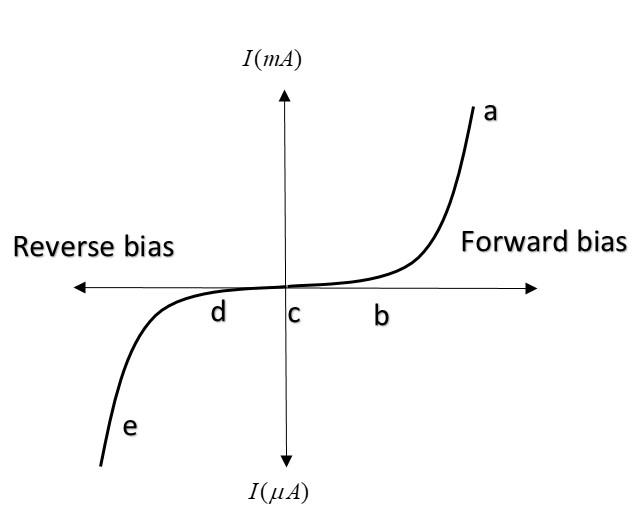
The graph given represents the IV characteristics of a Zener diode. Which part of the
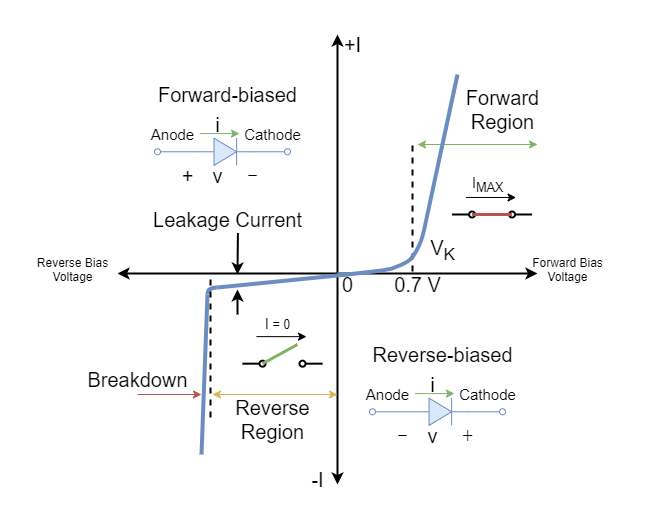
Because the diode is a passive device, the I-V curve for a diode is obtained by a linear voltage sweep and is shown in Figure 1. When the applied voltage across the diode is greater than zero, i.e., V D > 0 V D > 0, the diode is said to be forward-biased.
Diodes SparkFun Learn
Abstract. Current versus voltage graphs, also known as I-V curves, are commonly used to characterize semiconductor devices. In diode datasheets, for example, manufacturers can measure these nonlinear devices and present it in graphical form to customers. These graphs also convey the device's AC resistance, which quantifies the current change.
Schottky Diode
An I-V curve (short for 'current-voltage characteristic curve'), is a graphical representation of the relationship between the voltage applied across an electrical device and the current flowing through it. It is one of the most common methods of determining how an electrical device functions in a circuit.

pn junction diode Theory articles Community
The forward and reverse current voltage (IV) characteristics of a diode are generally compared on a single characteristic curve. The figure depicted under the section Forward Characteristic shows that Forward Voltage and Reverse Voltage are usually plotted on the horizontal line of the graph.

IV Curve Measurement System Ossila
The ideal diode i-v characteristic curve is shown below: Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): Ideal diode equation. The ideal diode equation is very useful as a formula for current as a function of voltage. However, at times the inverse relation may be more useful; if the ideal diode equation is inverted and solved for voltage as a function of current, we.
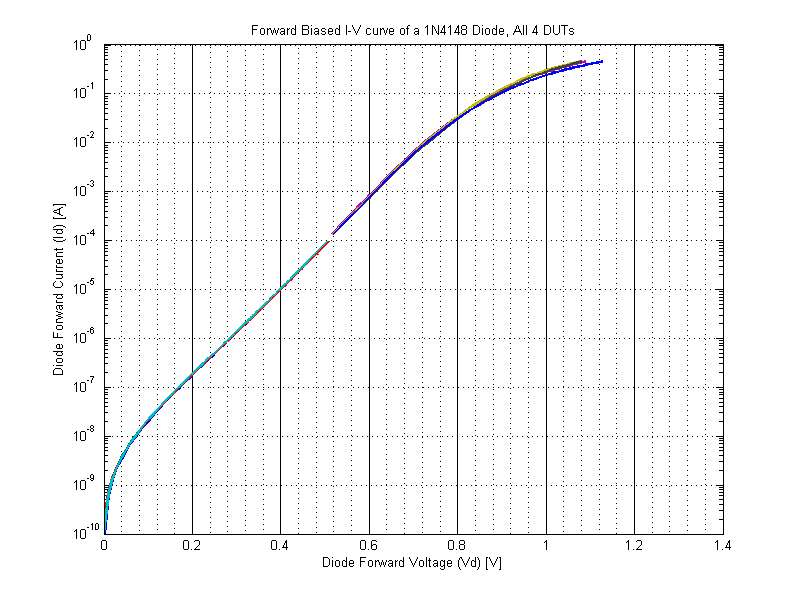
1N4148 Diode Forward Biased IV Curve 2N3904Blog
When we make a current-voltage plot (i-v curve) for an isolated resistor using Ohm's Law, the plot is straight line through the origin with a positive slope of 1/R. That's the i-v plot we get for a resistor all by itself. For the circuit in this video, the resistor is one of three components, connected between the diode and the voltage source.
How To Find Anode Cathode Of Diode 3 Testing Methods In Stepbystep
The normal current vs. voltage (I/V) curve of a Schottky barrier diode resembles that of a PN junction diode with the following exceptions: 1. The reverse breakdown voltage of a Schottky barrier diode is lower and the reverse leakage current higher than those of a PN junction diode made using the same resistivity semiconductor material. 2.
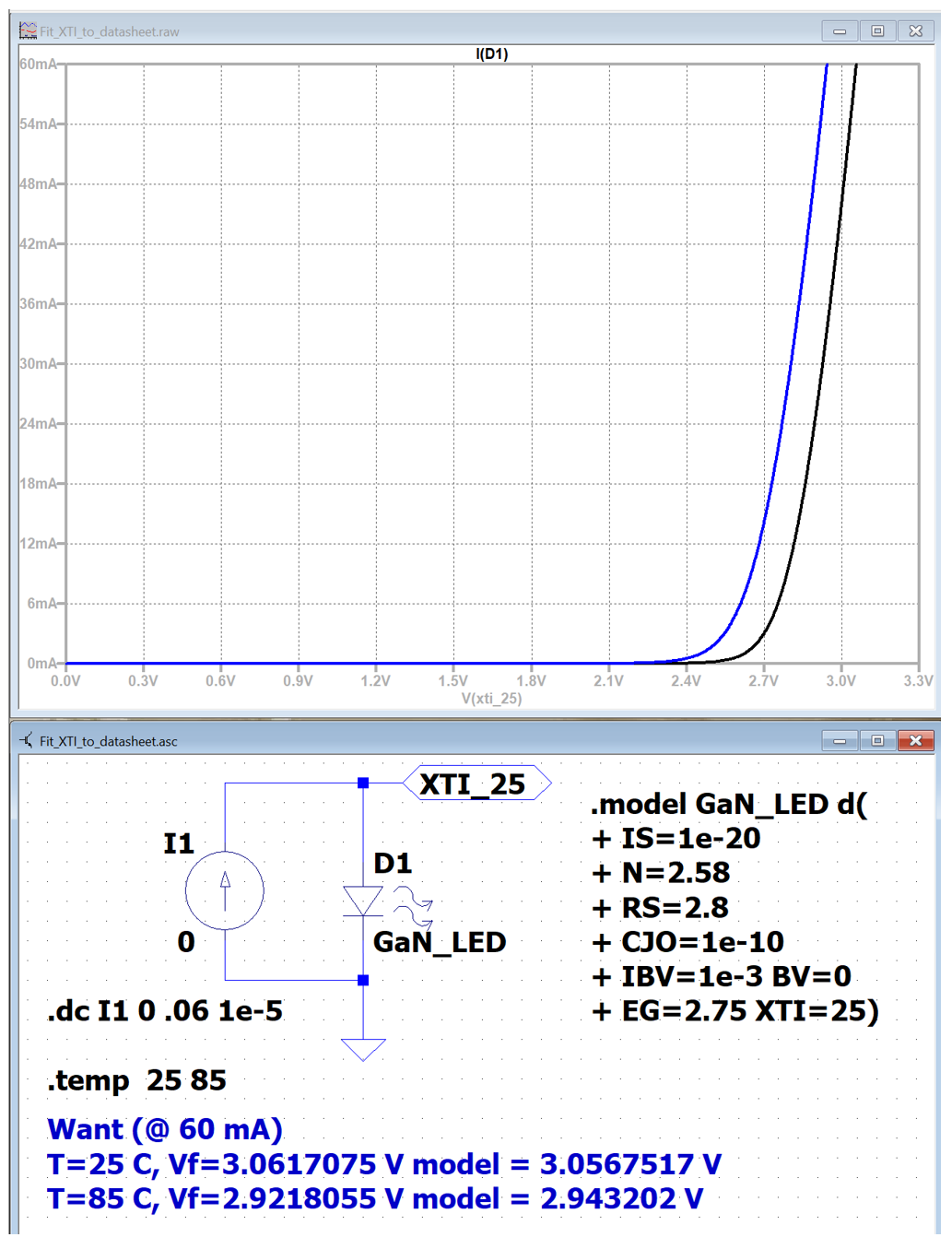
Electrical Can I model temperature dependent LED IV characteristics with Spice? Luminus Devices
The Shockley diode equation, or the diode law, named after transistor co-inventor William Shockley of Bell Labs, models the exponential current-voltage (I-V) relationship of semiconductor diodes in moderate constant current forward bias or reverse bias : where is the diode current, is the reverse-bias saturation current (or scale current),
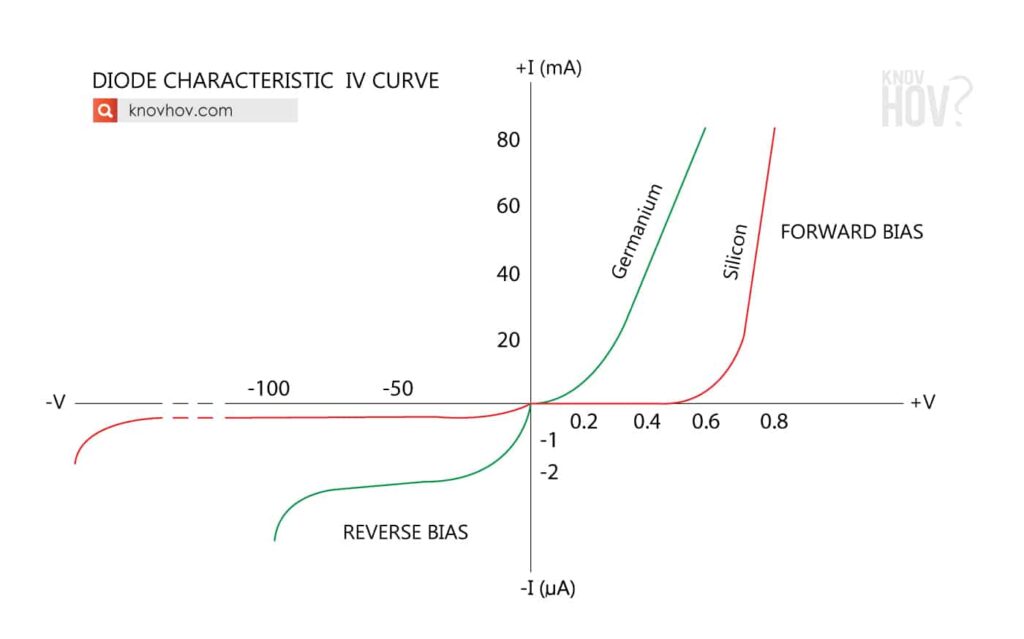
Silicon Diode IV Curve Electrical Academia
A diode is something that conducts current in one direction, and does not conduct current in the other direction. And the symbol we use for a diode looks like this. It has this big arrow here, that points in the direction of the forward current. One way to understand how a diode works is to draw an IV curve for it.

What Is A Reverse Diode
The diode equation gives an expression for the current through a diode as a function of voltage. The Ideal Diode Law, expressed as: I = I 0 ( e q V k T − 1) where: I = the net current flowing through the diode; I0 = "dark saturation current", the diode leakage current density in the absence of light;

Diodes Practical EE
Diode Characteristic Curve. The characteristic curve of a junction diode is also called an I-V Curve. It is typically a graph showing the current flow at different forward voltages. The current is typically on the y-axis, and the voltage on the x-axis. This type of graph provides engineers with a visual record of the operating characteristics.